Overview
An ultrasonic sensor is an electronic device used to measure distance or detect objects by emitting ultrasonic sound waves and analyzing the echoes that return. These sensors operate using high-frequency sound waves that are above the human hearing range (typically above 20 kHz).
How It Works
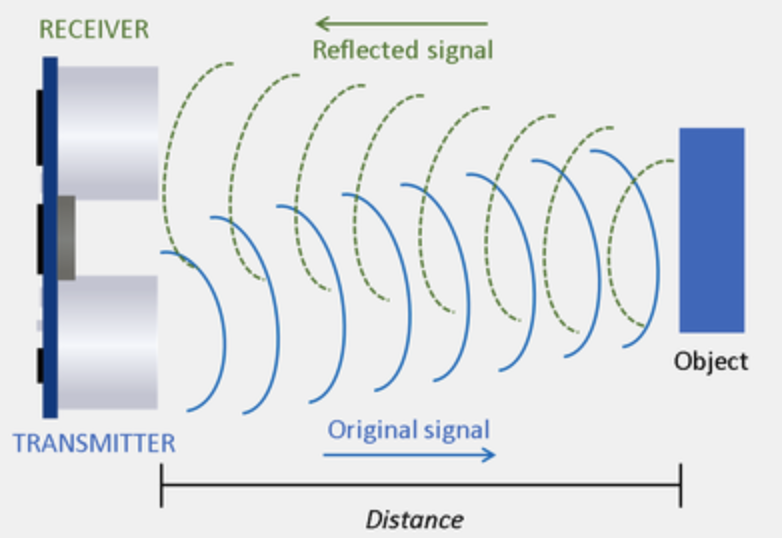
- Emission: The sensor’s transmitter emits ultrasonic waves.
- Reflection: The waves travel through the air until they hit an object and reflect back.
- Reception: The sensor’s receiver detects the reflected waves (the echo).
- Calculation: The sensor calculates the distance using the following formula. Here, the time represents the total duration for the sound wave to travel to the object and return. Dividing by 2 accounts for the round trip of the wave.
$$ Distance = \frac{Speed\ of\ Sound \times Time}{2} $$
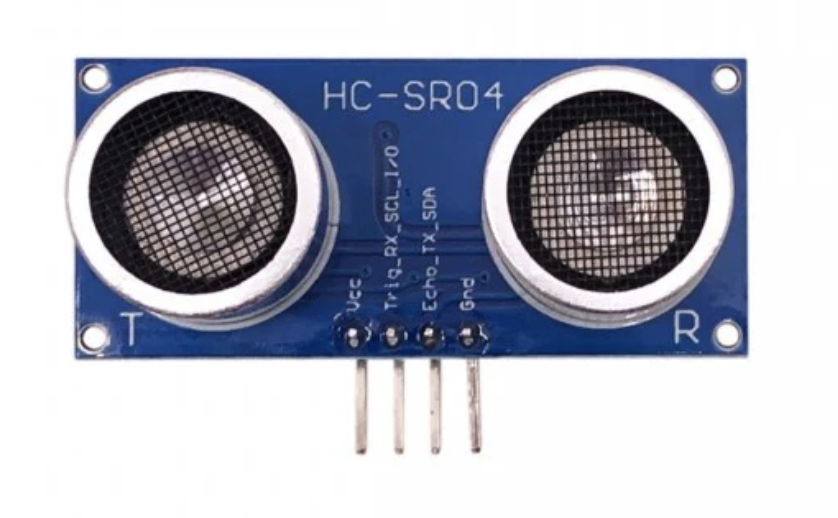
HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
The HC-SR04 is a popular and affordable ultrasonic distance sensor used in various DIY electronics and robotics projects. It measures the distance to an object by emitting ultrasonic waves and calculating the time it takes for the echo to return.
The standard HC-SR04 sensor typically operates at 5V, making it incompatible with the ESP32’s 3.3V logic level. To use the HC-SR04 with an ESP32, you need a logic level converter to act as a signal bridge between the two devices.
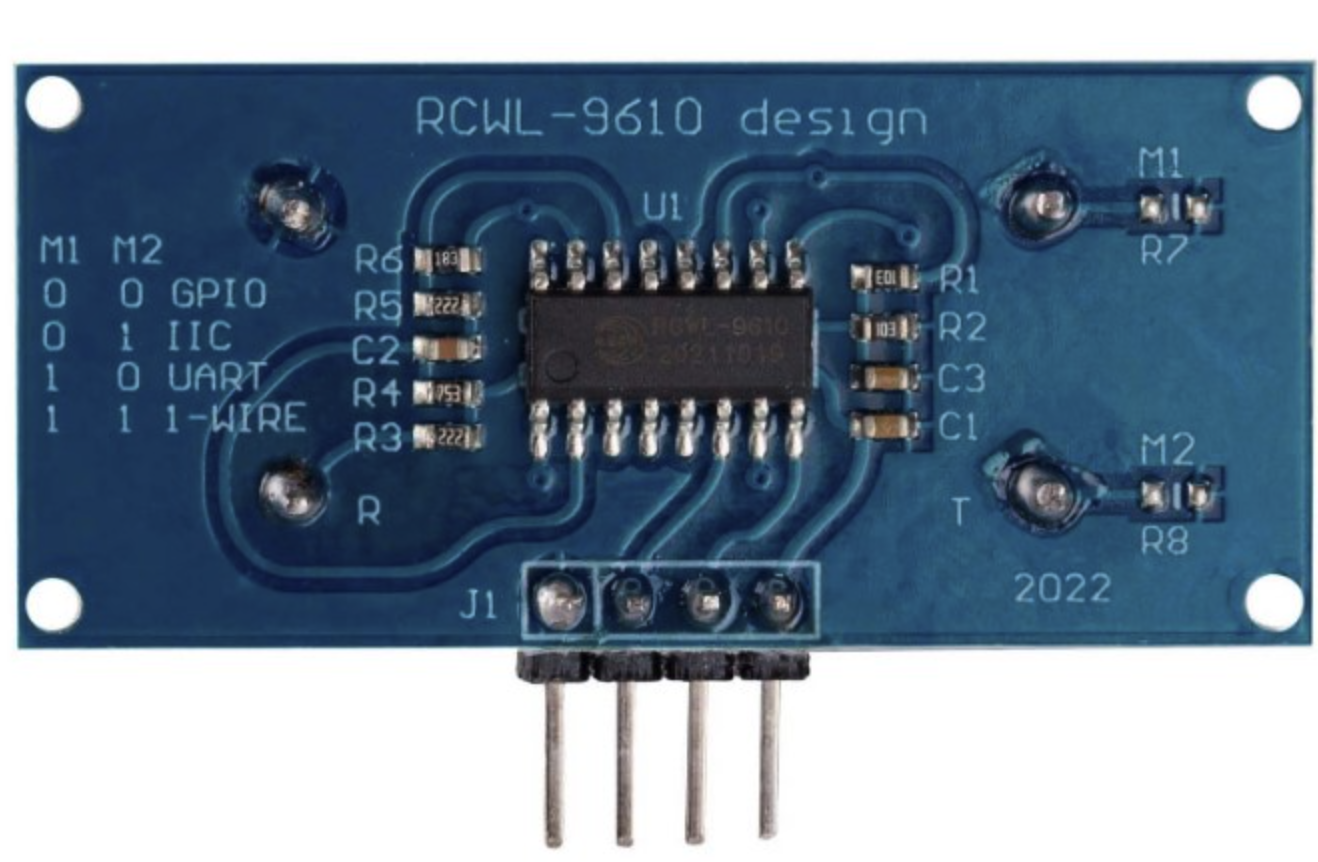
For compatibility with 3.3V logic MCUs like the ESP32, a better option is the HC-SR04 sensor with the RCWL-9610 design.
The HC-SR04 with the RCWL-9610 design is an upgraded version of the standard HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor. The key difference is the inclusion of the RCWL-9610 IC, which allows the sensor to work with both 3.3V and 5V logic levels. This feature makes it particularly suitable for microcontrollers like the ESP32 or ESP8266, which operate at 3.3V logic, without requiring a separate logic level converter.
Here is the front and back view of the HC-SR04 with RCWL-9610 Design.

Pinout
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply (3.3V or 5V) |
| Trig | Trigger input signal Setting this pin to HIGH for 10µs, the sensor initiates an ultrasonic burst. |
| Echo | Echo output signal The Echo pin goes high when the ultrasonic burst is sent and stays high until the echo is received, then it goes low. The duration the Echo pin stays high is used to calculate the distance. |
| GND | Ground |
Key Features
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V-5V DC
- Operating Current: ~15mA
- Measurement Range: 2 cm to 400 cm (0.78 inches to 13 feet)
- Accuracy: ±3 mm
- Trigger Input Signal: 10us TTL pulse
Pin Functions
The HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor measures distance by sending out sound waves and measuring how long it takes for them to bounce back. Here’s how it works in simple terms:
Trigger (Trig) Pin
The MCU send a small pulse (around 10 microseconds) to the Trig pin to tell the sensor to start. This pulse makes the sensor send out an ultrasonic sound wave.
Echo Pin
After the wave is sent, the sensor listens for the sound to bounce back (echo). The Echo pin stays high while the sensor waits for the echo. Once the echo is received, the pin goes low.
The sensor measures how long the Echo pin stays high. The longer it stays high, the farther away the object is. Using the time it takes for the echo to return, you can calculate the distance to the object.
In summary, the Trig pin triggers the sound wave. The Echo pin tells MCU how long it took for the sound wave to return, which helps calculate the distance.

